Creating and Using Droplets
Droplets allow third-party services to be used with the Fluid platform. Each Droplet is created and maintained by its creator company. Droplets can be used internally by the creator company or can be made available for use by other companies in the Droplet Marketplace.
Creating a Droplet
To create a Droplet, you need to have a Fluid account with access to the Fluid API.
Once you have access to the Fluid API, you can create a Droplet by making a POST request to the /api/droplets endpoint.
- Production server with company subdomain https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets
- Local development server http://fluid.lvh.me:3000/api/droplets
- curl
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Python
- Java
- C#
- PHP
- Go
- Ruby
- R
- Payload
curl -i -X POST \ https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN_HERE>' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "droplet": { "name": "string", "embed_url": "string", "settings": { "marketplace_page": { "title": "string", "summary": "string", "logo_url": "string" }, "details_page": { "title": "string", "summary": "string", "logo_url": "string", "features": [ { "name": "string", "summary": "string", "details": "string", "image_url": "string", "video_url": "string" } ] }, "service_operational_countries": [ "string" ] }, "categories": [ "string" ] } }'
A payload for creating a Droplet could look like this:
{ "droplet": { "name": "My Droplet", "embed_url": "https://my-company.com/embed", "active": true, "settings": { "marketplace_page": { "title": "My Droplet", "summary": "A Droplet for my company", "logo_url": "https://my-company.com/logo.svg", }, "details_page": { "title": "My Droplet", "summary": "A Droplet for my company", "logo": "https://my-company.com/big-logo.svg", "features": [ { "name": "Feature 1", "summary": "Feature 1 summary", "details": "Feature 1 details", "video_url": "https://my-company.com/feature-1.mp4" }, { "name": "Feature 2", "summary": "Feature 2 summary", "details": "Feature 2 details", "image_url": "https://my-company.com/feature-2.svg" }, ] } } } }
name
The name of the Droplet
embed_url
The URL of the page that will be embedded in the Fluid platform. When a company is using the Droplet, this is the page that will be shown to that company (in an iframe with the company's ID appended to the URL).
active
Whether the Droplet is active and can be used.
The settings determine how the Droplet will be displayed in the Fluid Marketplace
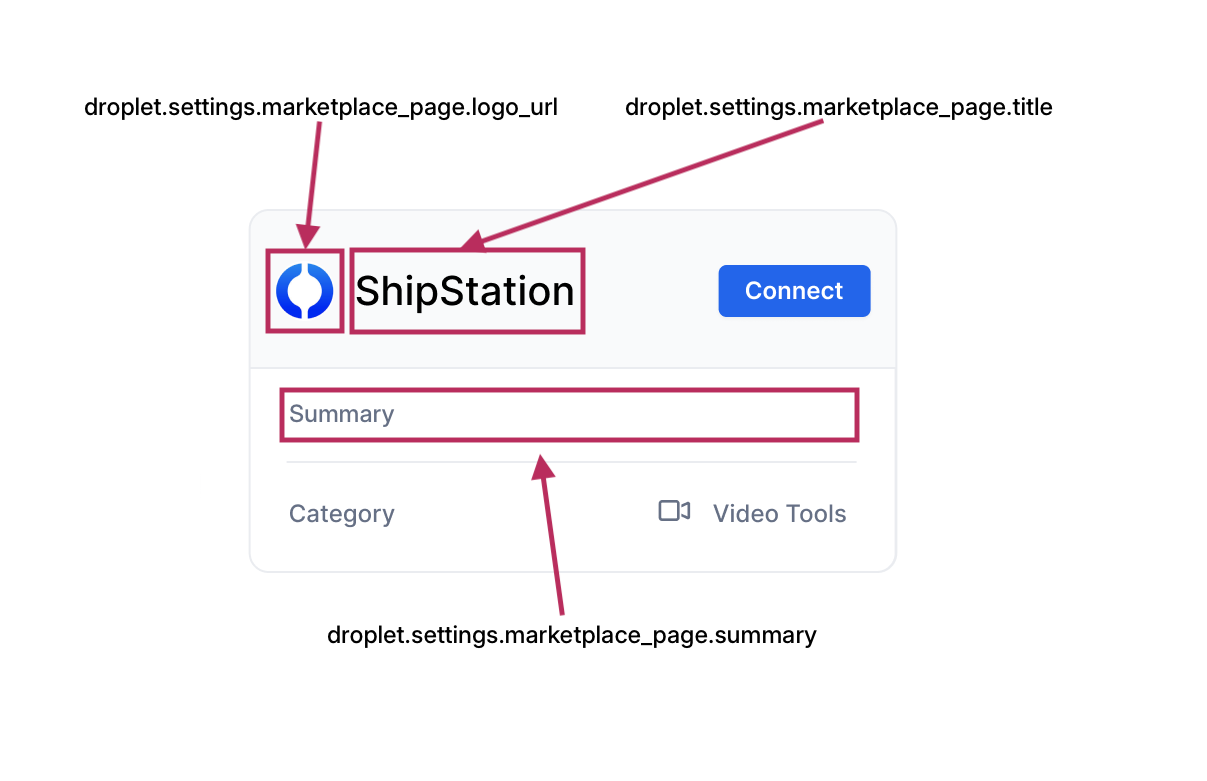
and what its individual details page will look like.
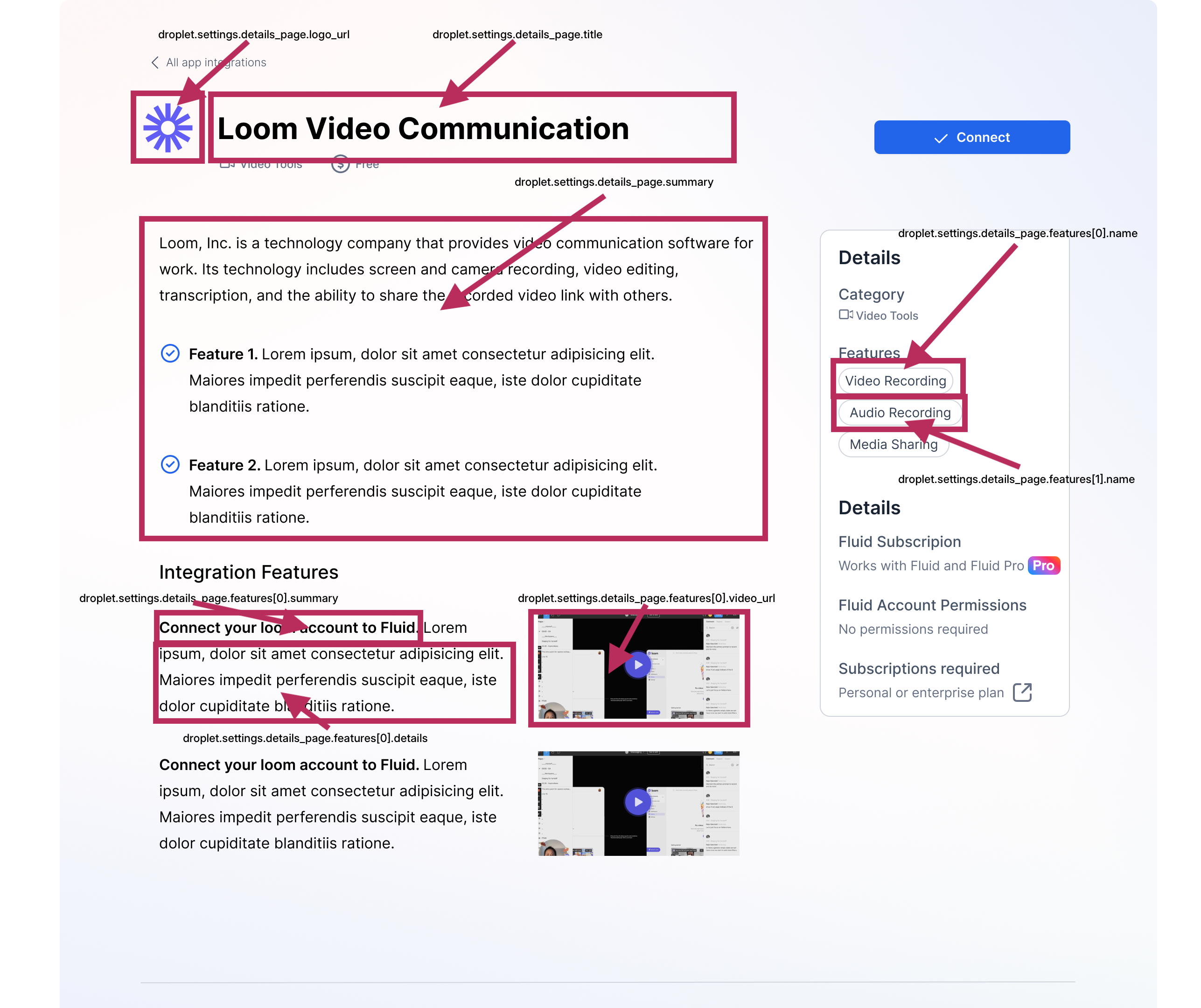
Note: Droplets won't be available in the Marketplace until they are approved by Fluid.
Updating a Droplet
To update a Droplet, you can make a PUT request to the /api/droplets/:droplet_uuid endpoint.
- Production server with company subdomain https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets/{uuid}
- Local development server http://fluid.lvh.me:3000/api/droplets/{uuid}
- curl
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Python
- Java
- C#
- PHP
- Go
- Ruby
- R
- Payload
curl -i -X PUT \ 'https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets/{uuid}' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN_HERE>' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "uuid": "string", "droplet": { "active": true, "publicly_available": true, "company_id": 0, "name": "string", "embed_url": "string", "settings": { "marketplace_page": { "title": "string", "summary": "string", "logo_url": "string" }, "details_page": { "title": "string", "summary": "string", "logo_url": "string", "features": [ { "name": "string", "summary": "string", "details": "string", "image_url": "string", "video_url": "string" } ] }, "service_operational_countries": [ "string" ] }, "categories": [ "string" ] } }'
A payload for updating a Droplet could look like this:
{ "droplet": { "name": "My Updated Droplet", "embed_url": "https://my-company.com/embed-updated", "active": false, "settings": { "marketplace_page": { "title": "My Updated Droplet", "summary": "A Droplet for my company", "logo_url": "https://my-company.com/logo.svg", }, "details_page": { "title": "My Updated Droplet", "summary": "A Droplet for my company", "logo": "https://my-company.com/big-logo.svg", "features": [ { "name": "Feature 1", "summary": "Feature 1 summary", "details": "Feature 1 details", "image_url": "https://my-company.com/new-feature-1.svg" }, { "name": "Feature 2", "summary": "Feature 2 summary", "details": "Feature 2 details", "image_url": "https://my-company.com/new-feature-2.svg", }, ] } } } }
Note: values that are not provided will be assumed to be null.
Listing Companies Using a Droplet
If you are the owner of a Droplet, you can list the companies using that Droplet with a GET request to the /api/droplets/:droplet_uuid/companies endpoint.
- Production server with company subdomain https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets/{uuid}/companies
- Local development server http://fluid.lvh.me:3000/api/droplets/{uuid}/companies
- curl
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Python
- Java
- C#
- PHP
- Go
- Ruby
- R
- Payload
curl -i -X GET \ 'https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplets/{uuid}/companies?page=0&per_page=100' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN_HERE>'
Understanding the Droplet Installation Flow
When companies install your droplet, a specific flow occurs that enables your droplet to interact with each installing company's data. Understanding this flow is critical for building droplets that respond to installation events.
Installation Flow Overview
Phase 1: One-Time Setup (Droplet Owner)
As the droplet owner, you need to register your droplet service to receive installation notifications. This is done once for your droplet:
- Register for installation webhooks on your company account:
curl -X POST "https://api.fluid.app/api/company/webhooks" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_OWNER_COMPANY_TOKEN" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "webhook": { "resource": "droplet", "event": "installed", "url": "https://your-droplet.com/api/webhooks", "http_method": "post" } }'
- Optionally register for uninstallation webhooks:
curl -X POST "https://api.fluid.app/api/company/webhooks" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_OWNER_COMPANY_TOKEN" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "webhook": { "resource": "droplet", "event": "uninstalled", "url": "https://your-droplet.com/api/webhooks", "http_method": "post" } }'
Important: These webhooks are registered on YOUR company (the droplet owner). When ANY company installs your droplet, Fluid will send the installation webhook to YOUR registered endpoint.
Phase 2: Per-Installation Flow (Each Installing Company)
When any company installs your droplet, the following occurs:
1. Fluid sends the droplet.installed webhook to your endpoint:
{ "resource": "droplet", "event": "installed", "company_id": 123, "company": { "fluid_company_id": 123, "droplet_uuid": "abc-123-def-456", "authentication_token": "dit_xyz789...", "name": "Installing Company Name", "fluid_shop": "company.myshopify.com" } }
2. Your droplet receives critical information:
fluid_company_id- The company's unique ID in Fluiddroplet_uuid- The unique installation IDauthentication_token- Token to act on behalf of this company (prefix:dit_)name- The company's display namefluid_shop- The company's shop identifier
3. Your droplet should:
- Store the company details and authentication token in your database
- Mark the company as active/installed
- Optionally register company-specific webhooks using their token
- Optionally create drop zones or other resources for this company
4. Example: Registering company-specific webhooks
Using the authentication_token received in the installation webhook, you can register webhooks specific to this company:
curl -X POST "https://api.fluid.app/api/company/webhooks" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer dit_xyz789..." \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "webhook": { "resource": "order", "event": "created", "url": "https://your-droplet.com/api/webhooks/company-123", "http_method": "post" } }'
Now your droplet will receive order.created events for this specific company.
Phase 3: Uninstallation Flow
When a company uninstalls your droplet:
{ "resource": "droplet", "event": "uninstalled", "company_id": 123, "company": { "fluid_company_id": 123, "droplet_uuid": "abc-123-def-456" } }
Your droplet should:
- Mark the company as inactive in your database
- Clean up any company-specific resources
Authenticating as a Company Using a Droplet
A DropletInstallation represents a company's use of a Droplet. It is created when a Company installs a Droplet.
You can see the details of a DropletInstallation for a Droplet your company owns with a GET request to the /api/droplet_installations/:uuid endpoint.
- Production server with company subdomain https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplet_installations/{uuid}
- Local development server http://fluid.lvh.me:3000/api/droplet_installations/{uuid}
- curl
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Python
- Java
- C#
- PHP
- Go
- Ruby
- R
- Payload
curl -i -X GET \ 'https://myco.fluid.app/api/droplet_installations/{uuid}' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN_HERE>'
The most important field in the response is the authentication_token, which can be used to authenticate as the company using the Droplet (it begins with the prefix dit).
When using the API you can authenticate using the Authorization header with the value Bearer <authentication_token>, e.g. Authorization: Bearer dit_12s34b5f678d90.
Note: While you can fetch installation details via the API, the recommended approach is to receive the
authentication_tokenautomatically via thedroplet.installedwebhook as described above.
Identifying Which Company is Using Your Droplet
When a company accesses your droplet through the Fluid interface, you need to identify which company is making the request. Fluid provides company context through URL parameters.
The DRI (Droplet Request Identifier) Parameter
When your droplet's embed_url is loaded in the Fluid interface, Fluid automatically appends a dri (Droplet Request Identifier) parameter:
Your configured embed_url:
https://your-droplet.com/embed
Actual URL loaded by Fluid:
https://your-droplet.com/embed?dri=abc123xyz789
The dri parameter is a unique identifier that maps to a specific DropletInstallation. You can use it to:
- Look up the company in your database (you stored this during installation)
- Retrieve the authentication token for this company
- Make API calls on behalf of this company
- Load company-specific settings and data
Example flow:
1. Extract dri from request: ?dri=abc123xyz789 2. Query your database: SELECT * FROM companies WHERE droplet_uuid = 'abc123xyz789' 3. Retrieve: company_id, authentication_token, settings 4. Use authentication_token to call Fluid API for this specific company
This pattern allows your droplet to serve multiple companies from a single service, with proper data isolation and authentication for each.
Creating Drop Zones from Your Droplet
Drop zones allow you to embed content from your droplet directly into specific locations within the Fluid interface (e.g., checkout page, product page). Your droplet can automatically create drop zones during installation.
What are Drop Zones?
Drop zones are embedded iframes that appear in predefined locations throughout the Fluid interface. Common locations include:
above_fast_checkout- Above the checkout buttonbelow_product_details- Below product informationcart_sidebar- In the shopping cart- And more (see Drop Zone Documentation)
Local Development and Testing
When developing your droplet locally, you need a way to receive webhooks from Fluid. Using a tunneling service like ngrok allows you to expose your local development server to the internet.
Setting Up ngrok for Droplet Development
1. Install ngrok:
# Linux/WSL sudo snap install ngrok # macOS brew install ngrok # Windows # Download from https://ngrok.com/download
2. Start your local droplet server:
# Your development server on port 3000, 3002, etc. npm run dev # or python manage.py runserver # or whatever your stack uses
3. Start ngrok tunnel:
ngrok http 3000
4. Copy the HTTPS URL from ngrok:
Forwarding https://abc123.ngrok.io -> http://localhost:3000
5. Register webhook with ngrok URL:
curl -X POST "https://api.fluid.app/api/company/webhooks" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_OWNER_COMPANY_TOKEN" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "webhook": { "resource": "droplet", "event": "installed", "url": "https://abc123.ngrok.io/api/webhooks", "http_method": "post" } }'
6. Test installation:
- Install your droplet through the Fluid interface
- Watch webhook arrive in your local server
- View requests in ngrok inspector:
http://localhost:4040
Benefits of Local Development with ngrok
✅ Real webhook payloads from Fluid production
✅ Instant debugging with breakpoints in your code
✅ Request inspection via ngrok web interface
✅ No deploy cycle - test changes immediately
✅ Works with any tech stack - language agnostic
ngrok Best Practices
- Use authtoken for persistent URLs across restarts (get from ngrok dashboard)
- Inspect traffic at
http://localhost:4040to see all webhook payloads - Replay requests from the ngrok inspector for rapid testing
- Update webhook URL in Fluid when your ngrok URL changes
- Use https URLs only - Fluid requires secure webhook endpoints
Alternative: Local Testing Without ngrok
If you prefer not to use ngrok, you can:
- Deploy to a staging environment and test there
- Use webhook forwarding services like webhook.site or requestbin
- Mock webhook payloads in your tests (see example webhooks above)
Best Practices for Building Droplets
Data Management
- Store company data: Always persist company details and authentication tokens from the
droplet.installedwebhook - Isolate company data: Ensure each company's data is properly isolated in your database
- Clean up on uninstall: Remove company data and delete drop zones when processing
droplet.uninstalledwebhooks
Authentication
- Secure tokens: Store authentication tokens securely (encrypted at rest)
- Use company tokens: Always use the company-specific
authentication_tokenwhen making API calls on their behalf - Never share tokens: Each company's token should only be used for that company's operations
Webhooks
- Handle idempotency: Webhooks may be delivered multiple times, ensure your handlers can process the same event safely
Error Handling
- Graceful degradation: If your droplet service is down, it shouldn't break the company's Fluid experience
- Retry logic: Implement retry with exponential backoff when calling Fluid APIs
- Monitor health: Set up monitoring and alerting for your droplet service
Development Workflow
- Develop locally with ngrok for rapid iteration
- Test installation flow by installing/uninstalling multiple times
- Monitor production webhooks and API calls
Quick Start Checklist
When building a new droplet, follow this checklist:
- Create droplet via API or Fluid interface
- Configure
embed_urlfor your droplet's main UI - Set up webhook endpoint to receive
droplet.installedanddroplet.uninstalledevents - Register webhooks on your company (one-time setup)
- Implement installation handler to:
- Store company details and authentication token
- Create any necessary drop zones
- Register company-specific webhooks (if needed)
- Implement uninstallation handler to:
- Mark company as inactive
- Clean up resources
- Handle DRI parameter in your embed URL to identify company context
- Test locally with ngrok (optional)
- Deploy to production
- Submit for marketplace approval (if making publicly available)
Additional Resources
- Webhooks Guide - Complete webhook documentation
- Drop Zone External Usage - Drop zone integration details
- Fluid API Reference - Full API documentation
- Authentication Guide - Authentication patterns and best practices